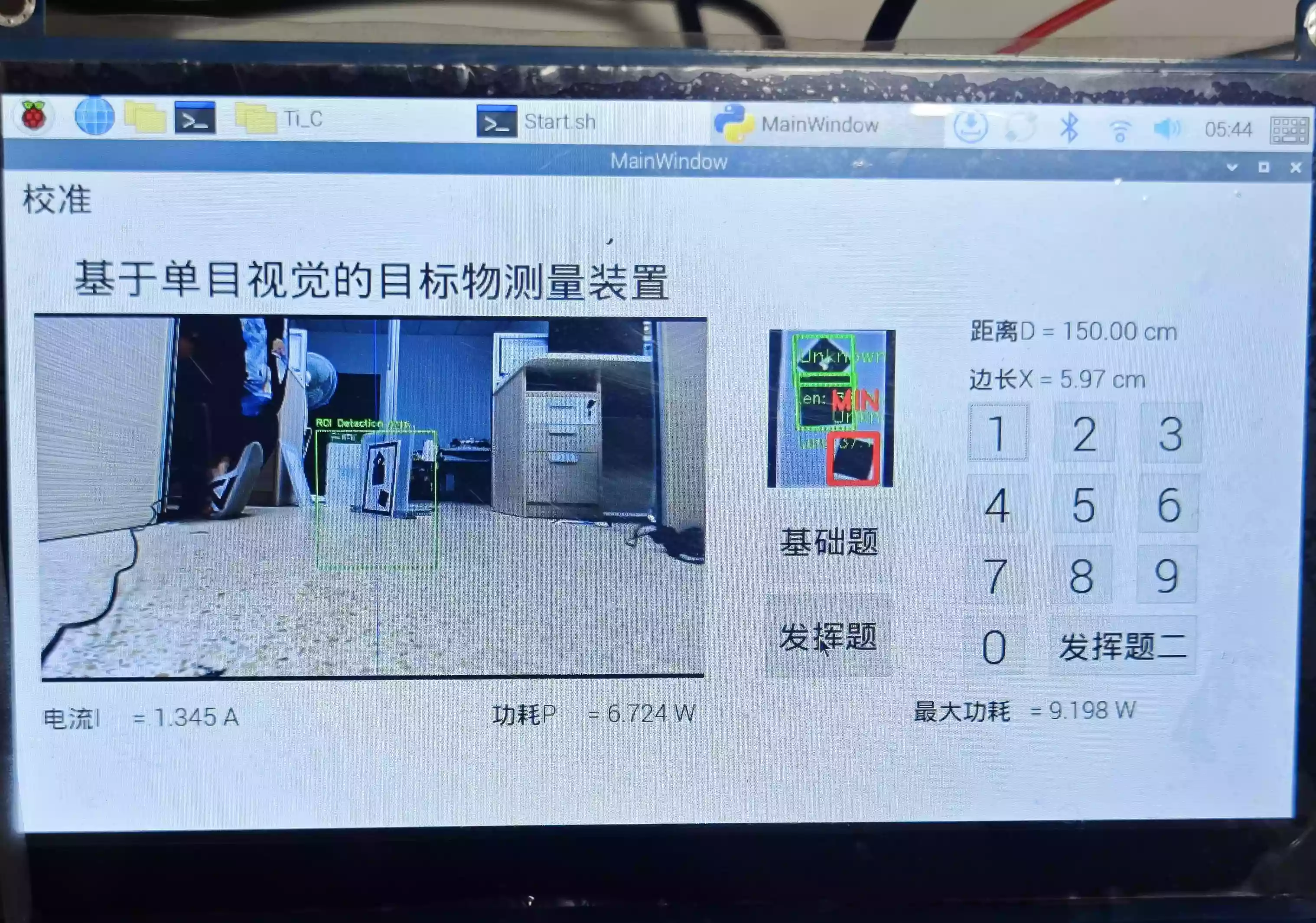
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| def find_a4_contour(image):
"""寻找矩形框,总计两个矩形框"""`
roi_x, roi_y, roi_w, roi_h = (526, 222, 227, 276)
roi_image = image[roi_y:roi_y+roi_h, roi_x:roi_x+roi_w]
cv2.rectangle(image, (roi_x, roi_y), (roi_x + roi_w, roi_y + roi_h), (255, 0, 0), 2)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(roi_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (5,5), 0)
edged=cv2.threshold(blur, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV + cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(edged, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
valid_contours = []
for cnt in contours:
area = cv2.contourArea(cnt)
if area > 5000:
valid_contours.append(cnt)
if len(valid_contours) < 2:
return None
sorted_contours = sorted(valid_contours, key=cv2.contourArea, reverse=True)
target = sorted_contours[1]
epsilon = 0.02 * cv2.arcLength(target, True)
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(target, epsilon, True)
if len(approx) == 4:
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(approx)
aspect_ratio = float(w) / h
if 0.35 < aspect_ratio < 0.75:
warped = get_topdown_view(roi_image, order_points(approx.reshape(4, 2)))
cv2.putText(image, f"W: {warped.shape[1]}, H: {warped.shape[0]}", (roi_x, roi_y - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.drawContours(roi_image, [approx], -1, (0, 255, 0), 2)
return warped
return None
|